List and Explain Any Four Different Parts of Plant Cell
There are various types of plant cells. Present and lies in the centre of the cell.

Plant Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Plant cells are generally larger than animal cells and are also less mobile.

. It is the largest organelle which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cells DNA. A plant cell is usually larger in size. Irregular or round in shape.
The part of a cell that contains RNA that helps in protein synthesis. The large and abundant vesicle of a plant cell is called a vacuole. Product or Line Layout.
They transport organic food prepared by the leaves to different parts of the plants. Protects the cell from osmotic swelling. Present and lies on one side of the cell.
Plant cells like animal cells are eukaryotic ie. Companion cells sieve tubes phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres. Up to 24 cash back The parts that make up the nucleus include the nuclear envelope nucleolus and chromosomes chromatin.
Have a cell membrane. Facilitates the movement of organelles. The parts of a plant cell and plant cell components which will be discussed are plant cell wall plant cell membrane smooth endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Further plant cells are green in color as they have unique pigments that aid in photosynthesis. These plant cells are eukaryotic and are rigid and harder than animal cells. Often have chloroplasts containing chlorophyll.
Plant cells are surrounded by a tough structure called the cell wall which is found outside of the cell membrane and is mainly made of cellulose. Phloem is a tissue that is formed of four different types of cells ie. It contains fluids and helps in storage of substances building material and water.
They allow the passage between two vegetal cells. Despite these plant and animal cells. Process or Functional Layout.
Have no cell wall. By structure the nucleus is. Animal cells are made up of four main parts namely nucleus cell membrane cytoplasm and mitochondria.
It confers shape and rigidity. Often irregular in shape. It is enclosed by a thin flexible plasma membrane only.
A plant cell consists of three distinct components. Plastids are a type of organelle found in plant cells and algae. Present but are very rare.
Plant cells have a large central vacuole that can occupy up to 90 of the cells volume. Do not contain plastids. Square or rectangular in shape.
The cell wall supports and protects plant cells giving them their characteristic rectangular or box-like shape. The most notable ones are parenchyma cells sclerenchyma cells collenchyma cells xylem cells and phloem cells. The cell wall central vacuole and chloroplasts are the distinguishing parts of a plant and animal cell.
The ribosome in a plant cell is found in the cytoplasm the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum the mitochondria and on chloroplasts. As such they are also semi-autonomous organelles. Contains the enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle.
Ribosome present in the animal cell also. The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose hemicellulose and pectin plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell turgor pressure. They also have a very unique cell division process whereby.
They contain membrane bound nuclei and cell organelles. An animal cell is comparatively smaller in size. Plant cells are very rigid because of their cell wall a component that does not exist within animal cellsThe plant cell wall was inherited from our prokaryotic ancestor and became a highly specialized part of the cell.
The plant cell has a well-defined cell wall made up of cellulose components plastids that perform photosynthesis and storage of carbohydrates in form of starch central vacuoles for regulating the cells turgor pressure and a nucleus which controls the cells general mechanisms including reproduction of the plant cells. The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. Have a cellulose cell wall outside the cell membrane.
The movement of organic food is bidirectional. Have prominent one or more vacuoles. Have only small vacuoles.
These cells help in the food production and metabolism part of the plant and. Animal cells may have many small vacuoles. The nuclear envelope also k now n as the nuclear membrane encloses the nucleus and nucleolus.
Four Main Types of Plant Layout. Structural support of cells. With all these parts plant cells.
Plant cell Animal cell. See the differences between plant cells and animal cells regarding cell organelles and other components. The vacuole is a very large organelle that can occupy up to 90 of the interior space of plant cells.
It is enclosed by a rigid cellulose cell wall in addition to plasma membrane. Keeping in view the type of industry and volume of production the type of layout to be selected is to be decided from the following. Like mitochondria plastids are membrane-bound organelles that contain nucleoids.
Although animal cells are similar to. The main parts of the plant cell include the cell wall cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus vacuole and chloroplasts. Plant cells have plasmodesmata which are pores between plant cell walls that allow molecules and communication signals to pass between individual plant cells.
I Cell wall ii Protoplasm and. Ribosome might be floating in the cytosol or within the. On the contrary plant cells lack centrioles and intermediate filaments which are present in animal cells.
Animal cells do not have plasmodesmata. There are different types of plastids that include chloroplasts chromoplasts gerontoplasts and leucoplasts. A plant cell differs from an animal cell in having certain distinctive structures cell wall vacuoles plasmodesmata and plastids.

Biology Quiz Plant Cell Parts And Functions Proprofs Quiz
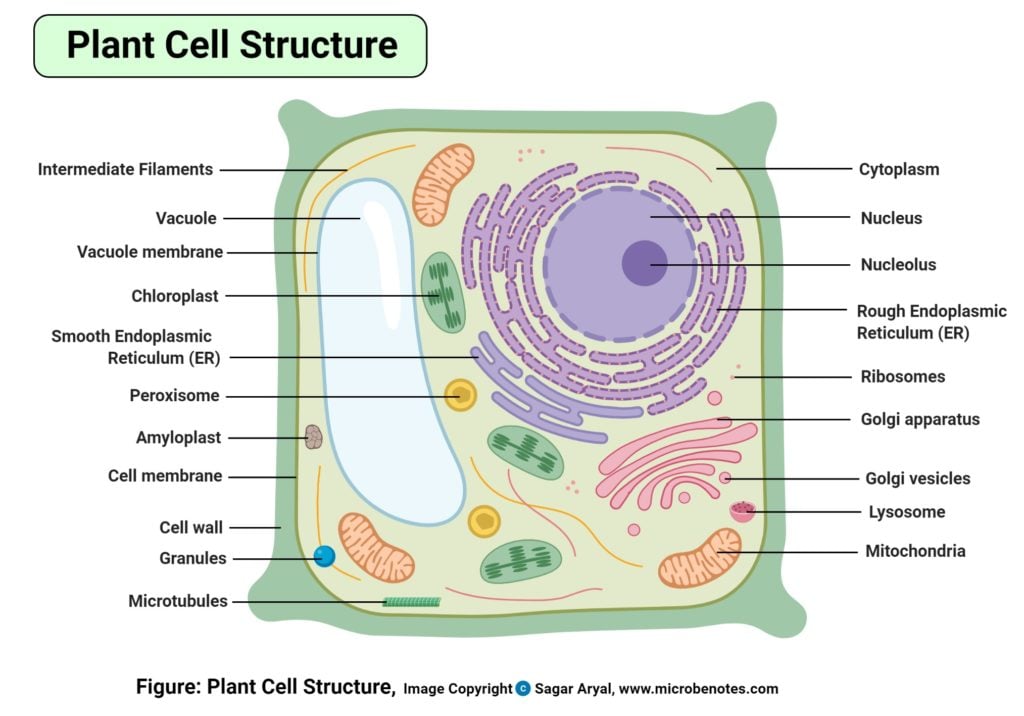
Plant Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions Labeled Diagram

Plant Cell Parts Functions What Is A Plant Cell Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Plant Cell Structure Parts Functions Types And Diagram

Plant Cell Definition Characteristics Facts Britannica
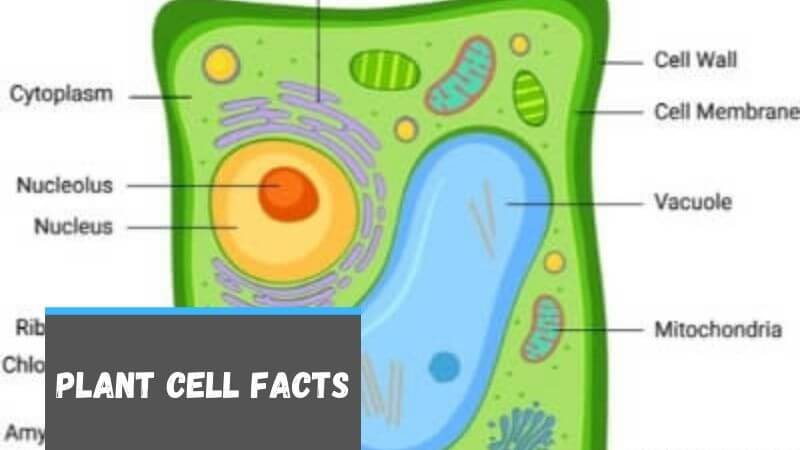
Plant Cell Facts For Kids Facts Just For Kids

Name The Parts Of A Plant Cell Plant And Animal Cells Cells Worksheet Animal Cell
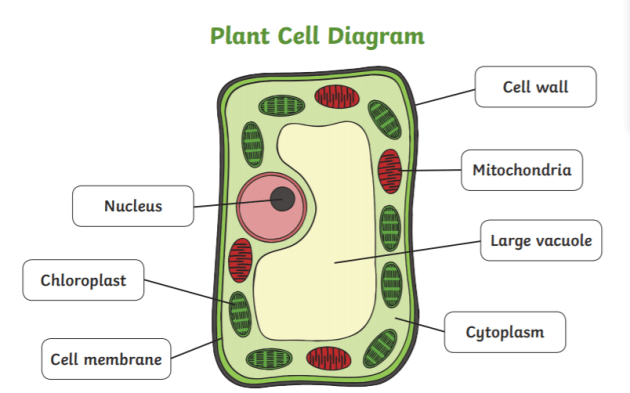

No comments for "List and Explain Any Four Different Parts of Plant Cell"
Post a Comment